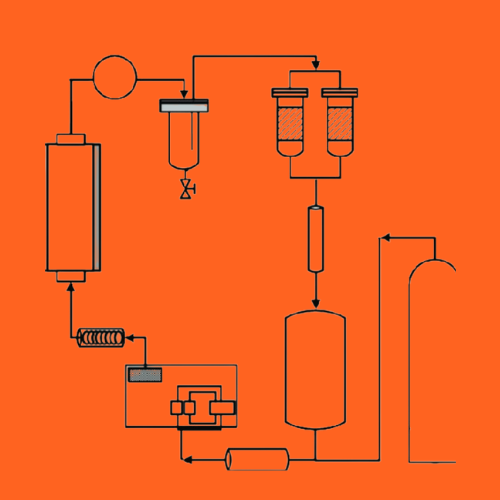
Linseed (flaxseed) oil extraction
The most common is mechanical cold-press
At present, the most common methods to extract flaxseed oil are mechanical pressing and solvent extraction. Fresh unrefined oil from pressing flaxseed has a nutty flavor and the colour varying from yellow to orange. As other edible oils on the market, it needs to be purified through the process of settling, alkali refining, degumming, bleaching, winterization and deodorization. Sometimes, home-made cold pressed oils can be consumed for cooking directly without further refining processing. Flaxseed oil extraction can be affected by several factors such as pretreatment of flaxseed, moisture content of flaxseed, cultivars, pressing conditions, etc.
Mechanical pressing for extracting flaxseed oil
Due to the high levels of ALA in flaxseed oil, it is necessary to avoid the high temperature during pressing. Generally, flaxseed oil obtained through cold pressing has high levels of ALA . Several types of flaxseed oil press have been developed, which are ranged from the simple hydraulic press to the more sophisticated continuous screw press. However, cold pressing can also bring negative impacts on the quality of oil. Due to low pressing temperature, microorganisms may not be killed completely during the pressing, which can decrease the quality of flaxseed oil. Additionally, due to low mass transfer under cold pressing, the contents of vitamins, phospholipids, phytosterols and antioxidants in oil are lower. These compounds are contributed to the stability of flaxseed oil. So, to prolong the shelf life of flaxseed oil, it is highly suggested that flaxseed oil should be kept in a container with dark color, and incorporated with the antioxidants.
To overcome the drawbacks of cold pressing, the ways such as flaxseed pressed under more aggressive conditions, heating or enzyme treatments for flaxseed prior to pressing, have been adopted utilized a single screw expeller to extract flaxseed oil. The results showed that the oil yield was improved with the increase of the number of consecutive pressing steps. Compared to the oils from three consecutive pressing steps, the oils with the highest ALA levels were obtained by double pressing showed that the oil yield for enzyme-assisted cold pressing flaxseed was higher than that for without-enzyme treated flaxseed. The extraction methods did not affect most of investigated physicochemical properties of flaxseed oils. Furthermore, the oil from enzyme-treated flaxseed showed better oxidative stability compared to that from without-enzyme treated flaxseed. The authors suggested that enzyme-assisted cold pressing was a good choice for extracting flaxseed oil with high yield and quality.

Linseed oil is suitable for
Body treatment and provides protection from UV radiation, enhances suntan. Besides Linseed oil is widely used in construction, finishing and even painting
Benefits of Linseed Oil
High in Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Much like flax seeds, flaxseed oil is loaded with heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
In fact, one tablespoon (15 ml) contains an impressive 7,196 mg of omega-3 fatty acids.
Specifically, flaxseed oil contains alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a form of omega-3 fatty acid that is only converted in small amounts to active forms of omega-3, like EPA and DHA.
If you aren’t getting enough DHA and EPA in your diet, most guidelines recommend at least 1,600 mg of ALA omega-3 fatty acids daily for men and 1,100 mg for women.
Just one tablespoon of flaxseed oil can meet and exceed your daily ALA needs.
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential to health and have been associated with benefits like reduced inflammation, improved heart health and protection for the brain against aging.
If you aren’t taking fish oil or getting one to two servings of fatty fish in your diet each week, flaxseed oil may be a good solution to help supplement your diet with the omega-3 fatty acids you need.
May Help Reduce Cancer Cell Growth
Although the current research is limited to test-tube and animal studies, there is some evidence that flaxseed oil may help reduce the growth of cancer cells.
In one animal study, mice were given 0.3 ml of flaxseed oil for 40 days. It was found to prevent the spread of cancer and the growth of lung tumors.
In another small animal study, flaxseed oil was shown to block the formation of colon cancer in rats.
Furthermore, test-tube studies have produced similar findings, with several studies showing that flaxseed oil reduced the growth of breast cancer cells.
Still, while these findings are promising, more research is needed to determine how these results may translate to humans.
Could Benefit Heart Health
Several studies have found that flaxseed oil could benefit heart health.
One study in 59 people compared the effects of flaxseed oil to those of safflower oil, a type of oil high in omega-6 fatty acids.
In this study, supplementing with one tablespoon (15 ml) of flaxseed oil for 12 weeks led to significantly lower blood pressure levels than supplementing with safflower oil.
High blood pressure can harm heart health, as it places extra strain on the heart, forcing it to work harder.
Flaxseed oil may also improve the elasticity of the arteries. Both aging and increased blood pressure are generally linked to decreases in elasticity.
These benefits are likely due to the high concentration of omega-3 fatty acids in flaxseed oil, as supplementing with it has been shown to significantly increase the amount of omega-3s in the blood.
What’s more, numerous studies have shown that omega-3 fatty acids improve heart health, with benefits such as reduced inflammation and lower blood pressure.
May Help Treat Constipation and Diarrhea
Flaxseed oil may be effective at treating both constipation and diarrhea.
A recent animal study showed that flaxseed oil acted as a laxative to promote regularity, all while acting as an antidiarrheal agent.
Another study gave 50 constipated patients on hemodialysis either flaxseed oil, olive oil or mineral oil.
After four weeks, flaxseed oil increased the frequency of bowel movements and improved stool consistency. Also, it was found to be as effective as both olive oil and mineral oil.
However, research on the effects of flaxseed oil on constipation and diarrhea is currently limited to animal studies and studies on people with specific conditions.
Additional studies are needed to evaluate its effectiveness in the general population.
May Improve Skin Health
Flaxseed oil may also help enhance skin health.
One small study had 13 women supplement with flaxseed oil for 12 weeks. At the end of the study, they experienced improvements in skin smoothness and hydration, while skin sensitivity to irritation and roughness had decreased.
A recent animal study showed that flaxseed oil had similar positive results.
Mice with dermatitis were given flaxseed oil for three weeks. The oil was shown to decrease symptoms of atopic dermatitis, such as redness, swelling and itching.
However, no studies have looked at the benefits of applying flaxseed oil to the skin of people. Nevertheless, there are numerous anecdotal reports of improvements in smoothness and reduced irritation after applying flaxseed oil.
May Reduce Inflammation
Thanks to its omega-3 fatty acid content, some research shows that flaxseed oil may help reduce inflammation in certain populations.
However, one analysis of 20 studies showed that flaxseed oil did not have an effect on inflammation in the general population.
Nevertheless, it significantly reduced levels of C-reactive protein, a marker used to measure inflammation, in obese people.
An animal study also found that flaxseed oil has potent anti-inflammatory properties.
Some studies indicate that flaxseed oil’s anti-inflammatory effects are equivalent to those of olive oil.
For example, one study in 37 people showed that flaxseed oil supplements didn’t affect any inflammatory markers in healthy, normal-weight adults, compared to olive oil.
While it seems that flaxseed oil may affect people differently, more research is needed to determine its effects on inflammation for the general population.
How to Use Linseed Oil
One of the best things about flaxseed oil is its versatility. For starters, it can easily be swapped for other types of oil in salad dressings, dips and sauces.
You can also add one serving (one tablespoon or 15 ml) into smoothies or shakes to add some flaxseed oil into your diet with minimal effort.
Keep in mind that flaxseed oil should not be used for cooking, as it does not have a high smoke point and can form harmful compounds when exposed to high heat.
In addition to being used in food, flaxseed oil can be applied to the skin to enhance skin health and increase skin moisture.
Alternatively, some people use flaxseed oil as a hair mask to promote growth and shine.
The Bottom Line
Flaxseed oil is high in omega-3 fatty acids and has been shown to have several health benefits, such as reduced blood pressure and improved regularity.
What’s more, flaxseed oil can be used in a variety of ways. It can be used as a replacement for other types of oils, added to foods or applied to your skin and hair.
Including just one or two servings of flaxseed oil in your daily routine is easy and could have numerous benefits for your overall health.

Where Linseed is harvested, Some interesting facts about Linseed
Linseed oil comes from flax seeds which are harvested from the same flax plant that produces the fibers used to make linen. Artists have been using linseed oil for centuries to make paints, mediums and varnishes. It is widely used today, not only in artist materials, but also for a wide range of industrial applications and as a dietary supplement. Linseed oil dries relatively fast and produces a durable, flexible paint film. The term alkali refined, when used in relation to oils, refers to the way the oil is extracted from the seed and subsequently clarified.
Linseed is grown to produce oil but the seed is used in an array of food products and is classed as superfood due to it’s rich content of essential fats Omega 3 and Omega 6, but all the Vitamins and Minerals and the fact it is High Fibre, Low Carbohydrate, Gluten Free, Low GI (glycemic index) and has the highest content of lignan than any other seed. This is why fresh linseed should be a part of everyone’s diet!
Linseed has been grown and used for thousands of years and can be dated back to the neolithic times. Used as an addition to food in either whole or ground form (Milled for us, as the husk of the seed needs breaking to release all the goodness inside. The whole seed will pass through as roughage otherwise) or the seed can be cold pressed to produce linseed oil (also sold as flaxseed oil).
This same plant has been used to grow the fibre from which linen has been made for thousands of years. Linseed was first cultivated for food in the ancient civilization of Mesopotamia. Located in the Middle East over nine thousand years ago.
History. Linseed comes from the flax plant (also known as Linum usitatissimum), a small plant that can grow up to about two feet in height. It has been cultivated all around the world, but it roots can be traced back to Egypt where it was most likely grown first, pretty much since the beginning of civilization.
Currently flax is produced on about 12 million acres globally with the largest areas of production in Kazakhstan, Russia, Canada and China. Flax was first introduced to the United States by colonists, primarily to produce fiber for clothing.
HISTORY
Linseed is one of the earliest crops cultivated by man and has so many uses, as you’re about to discover. Fabrics made from flax have been found in Swiss lake dwellings, dating back to 8000 BC and it has been regarded as a health food for centuries. Purportedly, in 8th Century Europe, King Charlemagne passed a law which stated that people MUST eat it! This is just one of the fabulous facts about linseed.
HEALTH BENEFITS
Linseed is known as one of the richest plant sources of Omega 3 fatty acids. These are essential for our health and King Charlemagne knew this which is why he wanted his people to be super healthy. What a thoughtful king! It’s also fabulous for heart health and rich in fibre and minerals. Research is still being done but linseed has also been known to help people with other conditions such as joint pain, asthma, stress, allergies, constipation, eczema, acne, psoriasis, cholesterol levels and prostate problems.
GOLDEN AND BROWN
Did you know that linseed comes in two forms? There are the golden and the brown varieties of the flax plant and they are shown to have equal nutritional benefits. Canada produces the brown varieties and they are the world’s biggest producer. This brown seed is commonly sold in ground form and converted to oil. The golden varieties are predominantly produced in the USm with Dakota Gold being a popular one with US producers.
LUSCIOUS LIGNANS
Linseed is one of nature’s riches sources of lignans. These have two effects on the body. They’re an antioxidant and as such have been said to help with the battle against cancer and in particular breast cancer. They also modulate oestrogen levels in women, which means they can act as natural form of hormone therapy and help when the hot flushes attack during menopause.
BIG BUSINESS
Linseed really is a super seed. The UK is the world’s fifth largest producer with around 70,000 tonnes grown here annually. There is obviously the huge market for human consumption but it’s also used in animal feed to boost their health and in turn, ours.
LOVELY LINEN
Did you know that those beautiful linen trousers you’re wearing are made from the fibers of the stalk of the flax plant? We often associate linen with bedding and clothing but in history it has been used for sails on ships and to wrap mummies in Ancient Egypt. Linen is so strong that 3,000 year old linen has been found intact!
WONDERFUL WORDS
Ever heard of the phrases “flaxen haired beauty” to describe a woman with beautiful blonde hair and the word “lingerie”? Well, they have their origins in the linseed. The “lining” in your jacket would have been made from, yes, you guessed it, linen! Linoleum is also named after the linseed oil which is used in its manufacture.
Is anyone else a fan of linseed? Perhaps you know some interesting facts about these mighty magical morsels of goodness.

